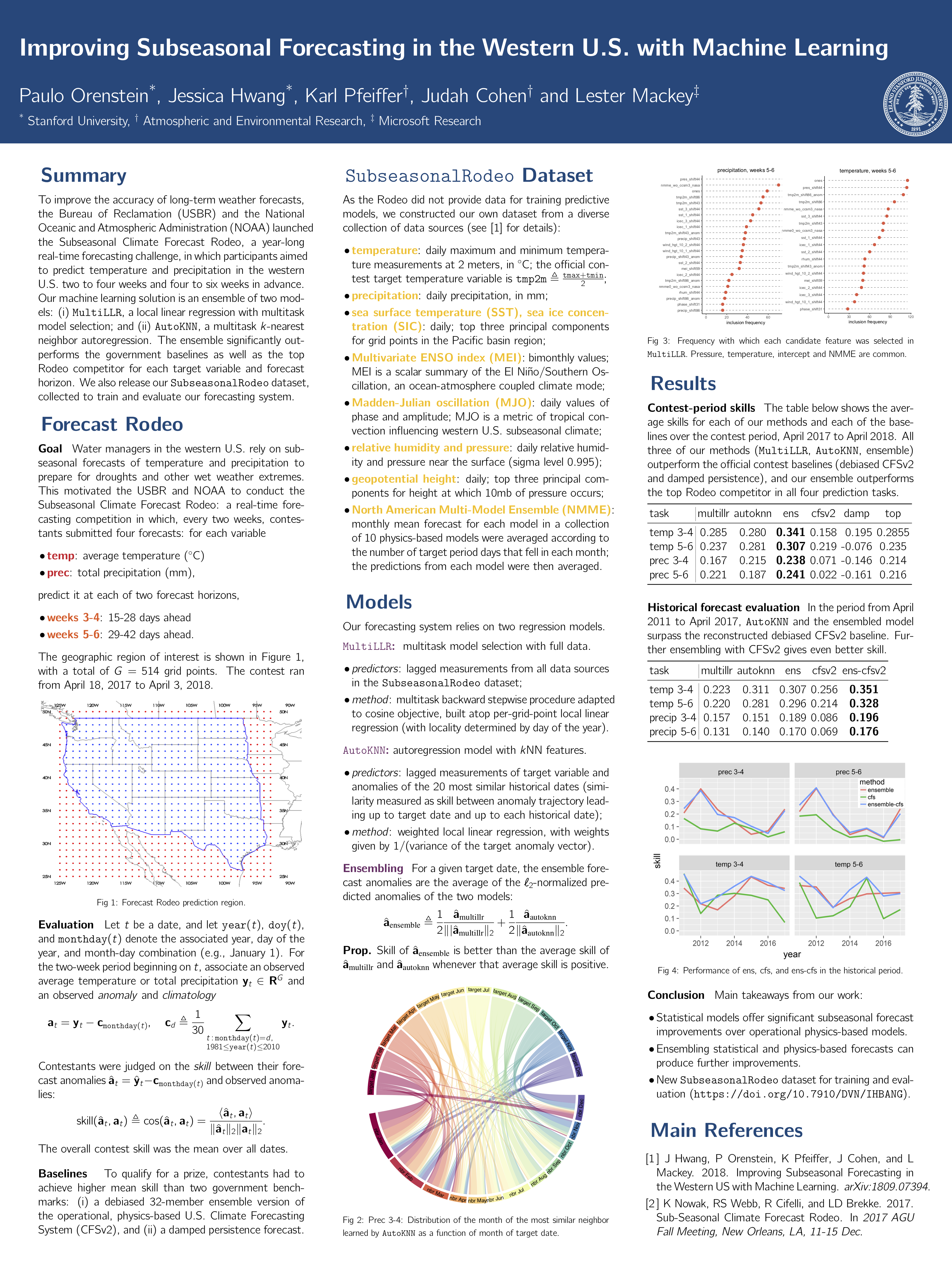
本文在『气象学家』同步推送传送门;美国西部地区的水资源管理极大地依赖于长期的温度和降水预报以应对干旱和其他的洪涝相关极端灾害天气。为了提升长期预报的准确性,美国垦务局和美国国家海洋和大气管理局(NOAA)发起了次季节气候预测的竞赛,长达一年的实时预报竞赛,参与者各显神通,旨在有技巧地提前预报美国西部地区2
4周和46周的温度和降水。在此,我们给出和评估了我们的机器学习方法,并发布了 SubseasonalRodeo数据集,用于训练和评估我们的预报系统。
Title:Improving Subseasonal Forecasting in the Western U.S. with Machine Learning
**标题**:**使用机器学习来改进美国西部地区的次季节预报 **
**作者**:Jessica Hwang**1***, Paulo Orenstein** 1**, Judah Cohen**2**, Karl Pfeiffer**2**, Lester Mackey**3**
**1**Department of Statistics, Stanford University Stanford, California2Atmospheric and Environmental Research Lexington, MA
3Microsoft Research New England Cambridge, MA
**会议**:" In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 2325-2335. ACM, 2019.
**DOI**: [**https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.07394**](https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.07394)
Poster预览(放大即可)
文章下载地址: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1809.07394.pdf
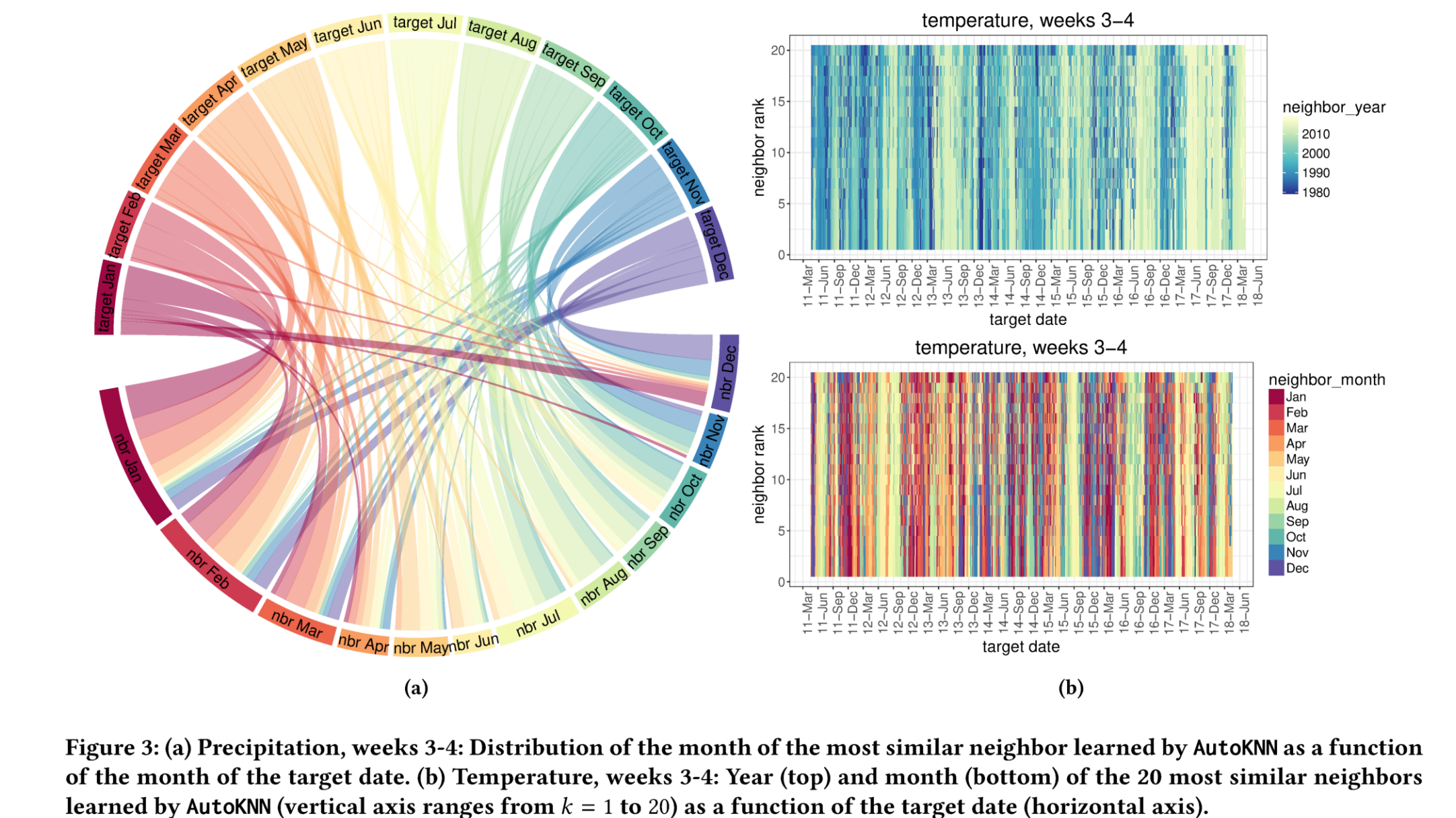
SubseasonalRodeo数据集
SubseasonalRodeo数据集下载地:https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.7910/DVN/IHBANG
作者的视频报告
From the MIT Statistics and Data Science Conference (SDSCon) 2019.
视频地址:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DbTn9vUYR_c
或者去公众号观看,传送门
Abstract
Water managers in the western United States (U.S.) rely on longterm forecasts of temperature and precipitation to prepare for droughts and other wet weather extremes. To improve the accuracy of these longterm forecasts, the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) launched the Subseasonal Climate Forecast Rodeo, a year-long real-time forecasting challenge in which participants aimed to skillfully predict temperature and precipitation in the western U.S. two to four weeks and four to six weeks in advance. Here we present and evaluate our machine learning approach to the Rodeo and release our SubseasonalRodeo dataset, collected to train and evaluate our forecasting system.
Our system is an ensemble of two regression models. The first integrates the diverse collection of meteorological measurements and dynamic model forecasts in the SubseasonalRodeo dataset and prunes irrelevant predictors using a customized multitask model selection procedure. The second uses only historical measurements of the target variable (temperature or precipitation) and introduces multitask nearest neighbor features into a weighted local linear regression. Each model alone is significantly more accurate than the debiased operational U.S. Climate Forecasting System (CFSv2), and our ensemble skill exceeds that of the top Rodeo competitor for each target variable and forecast horizon. Moreover, over 2011-2018, an ensemble of our regression models and debiased CFSv2 improves debiased CFSv2 skill by 40-50% for temperature and 129-169% for precipitation. We hope that both our dataset and our methods will help to advance the state of the art in subseasonal forecasting.
原文摘要
美国西部地区的水资源管理极大地依赖于长期的温度和降水预报以应对干旱和其他的洪涝相关极端灾害天气。为了提升长期预报的准确性,美国垦务局和美国国家海洋和大气管理局(NOAA)发起了次季节气候预测的竞赛,长达一年的实时预报竞赛,参与者各显神通,旨在有技巧地提前预报美国西部地区24周和46周的温度和降水。在此,我们给出和评估了我们的机器学习方法,并发布了 SubseasonalRodeo数据集,用于训练和评估我们的预报系统。
我们的系统是两个回归模型的集合。第一个模型融合了不同的气象观测数据集合动力模式预报结果到SubseasonalRodeo数据集中,使用自定义的多任务模型选择过程删除不相关的预报因子。第二个模型仅仅使用特定变量(温度或降水)的历史测量数据,并引入多任务最邻近特征到一个加权的局地线性回归中。每个模式各自都要显著地比CFSv2(去偏差准业务化的美国气候预报系统)要更加的准确,同时我们的集合技巧就每个目标预报量和预报水平都要全面超过Rodeo竞争对手。此外,在2011-2018期间,我们的回归模型与去偏差CFSv2的集合方案要比单一的去偏差CFSv2就温度预报的技巧提升了40%-50%,降水的预报提升了 129-169% 。我们希望我们的数据集合我们的方法将能够有助于促进先进的次季节预报。
图文
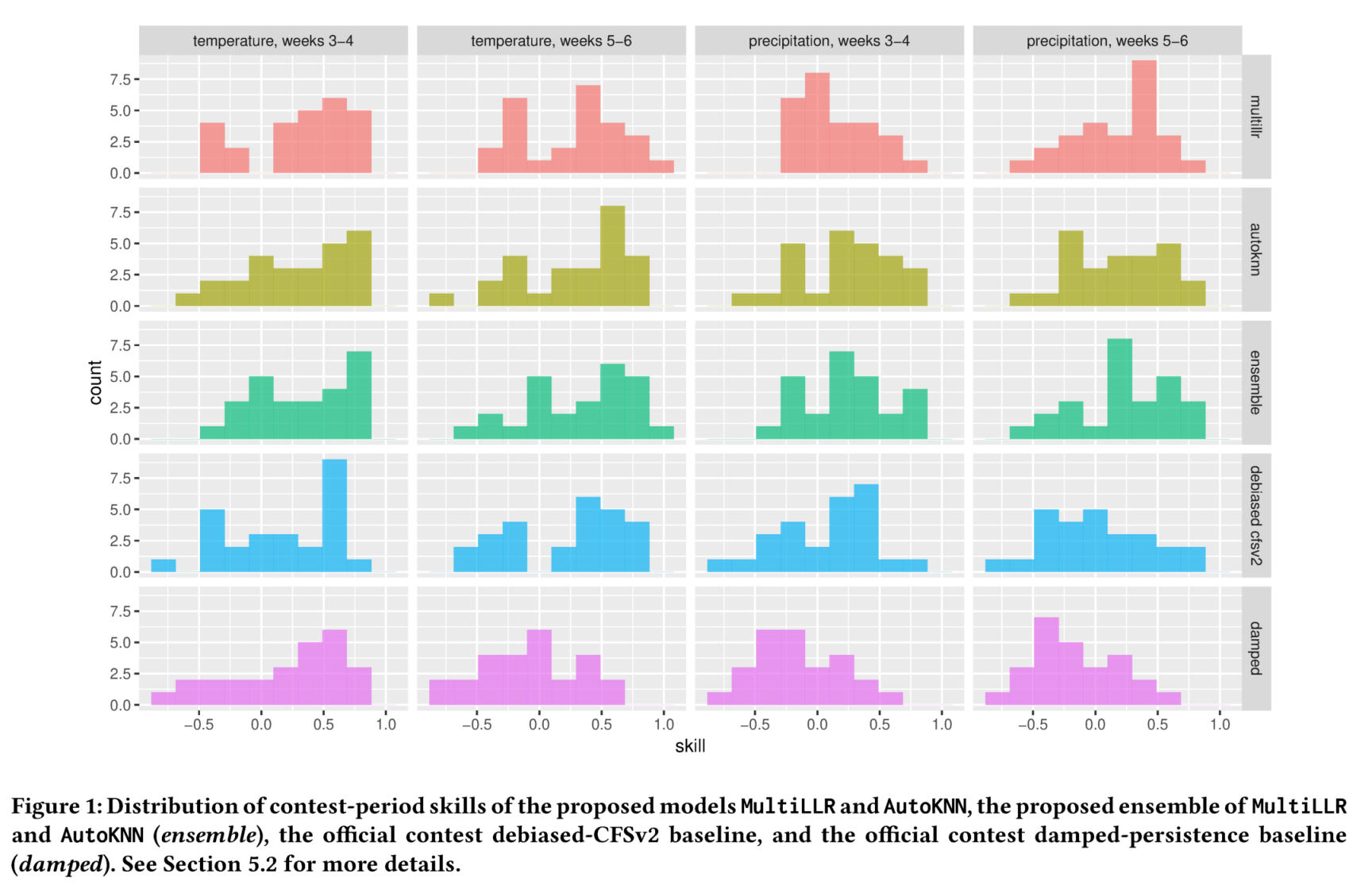
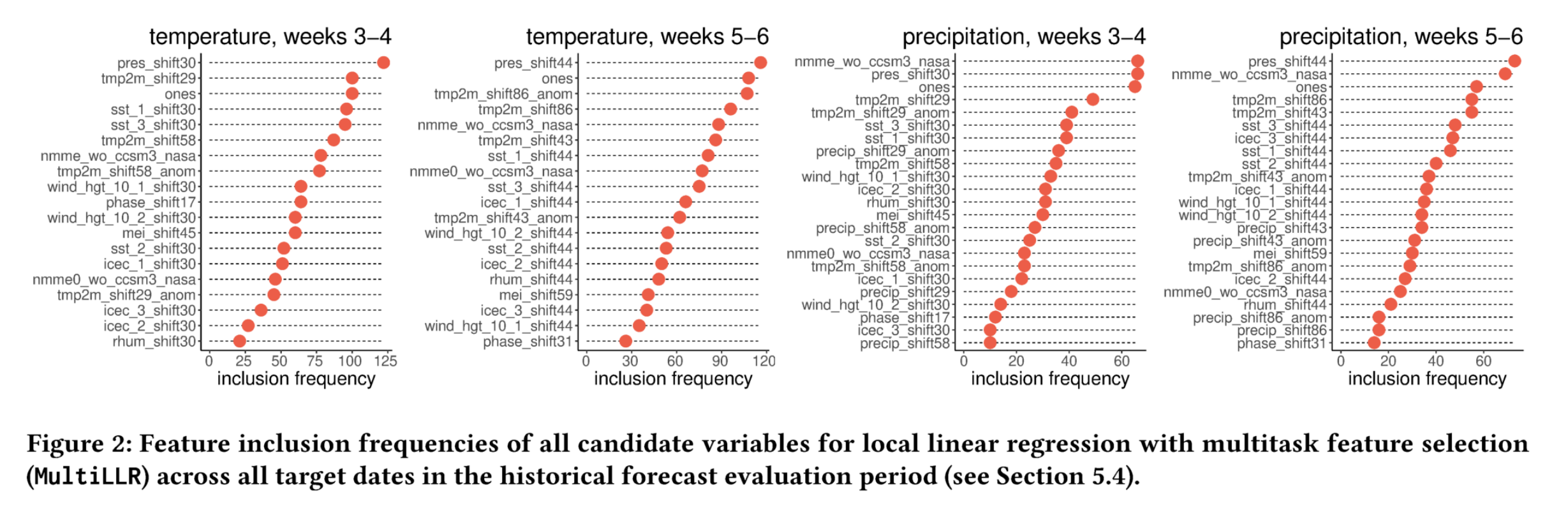

参考:
有任何问题都欢迎交流探讨,共同学习进步!


